本节引言:
前面两节我们学习的都是一些概念性的东西,Http的协议以及协议头的一些东东,而本节我们就要堆码了,而本节学习的是Android为我们提供的Http请求方式之一:HttpURLConnection,除了这种,还有一种还有一种HttpClient,后者我们会下一节讲!不过前者一旦请求复杂起来,使用起来非常麻烦,而后者我们Java抓包也经常会用到,是Apache的,毕竟不是谷歌亲儿子,而在4.4版本HttpURLConnection已被替换成OkHttp了!好吧,与时俱进,决定讲完HttpClient也来会会这个OkHttp!对了,一般我们实际开发并不会用HttpURLConnection和HttpClient,使用别人封装好的第三方网络请求框架,诸如:Volley,android-async-http,loopj等,因为网络操作涉及到异步以及多线程,自己动手撸的话,很麻烦,所以实际开发还是直接用第三方!!当然学习下也无妨,毕竟第三方也是在这些基础上撸起来的,架构逼格高,各种优化!好的,话不多说,开始本节内容!
1.HttpURLConnection的介绍
答:一种多用途、轻量极的HTTP客户端,使用它来进行HTTP操作可以适用于大多数的应用程序。虽然HttpURLConnection的API提供的比较简单,但是同时这也使得我们可以更加容易地去使用和扩展它。继承至URLConnection,抽象类,无法直接实例化对象。通过调用openCollection()方法获得对象实例,默认是带gzip压缩的;
2.HttpURLConnection的使用步骤
使用HttpURLConnection的步骤如下:
- 创建一个URL对象:URL url = new URL(https://www.baidu.com);
- 调用URL对象的openConnection( )来获取HttpURLConnection对象实例:HttpURLConnection conn = (HttpURLConnection) url.openConnection();
- 设置HTTP请求使用的方法:GET或者POST,或者其他请求方式比如:PUTconn.setRequestMethod("GET");
- 设置连接超时,读取超时的毫秒数,以及服务器希望得到的一些消息头conn.setConnectTimeout(6*1000);conn.setReadTimeout(6 * 1000);
- 调用getInputStream()方法获得服务器返回的输入流,然后输入流进行读取了InputStream in = conn.getInputStream();
- 最后调用disconnect()方法将HTTP连接关掉conn.disconnect();
PS:除了上面这些外,有时我们还可能需要对响应码进行判断,比如200:if(conn.getResponseCode() != 200)然后一些处理 还有,可能有时我们并不需要传递什么参数,而是直接去访问一个页面,我们可以直接用:final InputStream in = new URL("url").openStream();然后直接读流,不过这个方法适合于直接访问页面的情况,底层实现其实也是return openConnection().getInputStream(),而且我们还不能设置一些请求头的东东,所以要不要这样写,你自己要掂量掂量!
3.HttpURLConnection使用示例
这里我们主要针对GET和POST请求写两个不同的使用示例,我们可以conn.getInputStream()获取到的是一个流,所以我们需要写一个类将流转化为二进制数组!工具类如下:
StreamTool.java:
/** * Created by Jay on 2015/9/7 0007. */public class StreamTool { //从流中读取数据 public static byte[] read(InputStream inStream) throws Exception{ ByteArrayOutputStream outStream = new ByteArrayOutputStream(); byte[] buffer = new byte[1024]; int len = 0; while((len = inStream.read(buffer)) != -1) { outStream.write(buffer,0,len); } inStream.close(); return outStream.toByteArray(); }}接下来就可以开始撸我们的示例了!
1)HttpURLConnection发送GET请求代码示例
运行效果图:

核心部分代码:
布局:activity_main.xml
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="https://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:orientation="vertical"> <TextView android:id="@+id/txtMenu" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="48dp" android:background="#4EA9E9" android:clickable="true" android:gravity="center" android:text="长按我,加载菜单" android:textSize="20sp" /> <ImageView android:id="@+id/imgPic" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:visibility="gone" /> <ScrollView android:id="@+id/scroll" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:visibility="gone"> <TextView android:id="@+id/txtshow" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" /> </ScrollView> <WebView android:id="@+id/webView" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" /></LinearLayout>
获取数据类:GetData.java:
/** * Created by Jay on 2015/9/7 0007. */public class GetData { // 定义一个获取网络图片数据的方法: public static byte[] getImage(String path) throws Exception { URL url = new URL(path); HttpURLConnection conn = (HttpURLConnection) url.openConnection(); // 设置连接超时为5秒 conn.setConnectTimeout(5000); // 设置请求类型为Get类型 conn.setRequestMethod("GET"); // 判断请求Url是否成功 if (conn.getResponseCode() != 200) { throw new RuntimeException("请求url失败"); } InputStream inStream = conn.getInputStream(); byte[] bt = StreamTool.read(inStream); inStream.close(); return bt; } // 获取网页的html源代码 public static String getHtml(String path) throws Exception { URL url = new URL(path); HttpURLConnection conn = (HttpURLConnection) url.openConnection(); conn.setConnectTimeout(5000); conn.setRequestMethod("GET"); if (conn.getResponseCode() == 200) { InputStream in = conn.getInputStream(); byte[] data = StreamTool.read(in); String html = new String(data, "UTF-8"); return html; } return null; }}MainActivity.java:
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity { private TextView txtMenu, txtshow; private ImageView imgPic; private WebView webView; private ScrollView scroll; private Bitmap bitmap; private String detail = ""; private boolean flag = false; private final static String PIC_URL = "https://ww2.sinaimg.cn/large/7a8aed7bgw1evshgr5z3oj20hs0qo0vq.jpg"; private final static String HTML_URL = "https://www.baidu.com"; // 用于刷新界面 private Handler handler = new Handler() { public void handleMessage(android.os.Message msg) { switch (msg.what) { case 0x001: hideAllWidget(); imgPic.setVisibility(View.VISIBLE); imgPic.setImageBitmap(bitmap); Toast.makeText(MainActivity.this, "图片加载完毕", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show(); break; case 0x002: hideAllWidget(); scroll.setVisibility(View.VISIBLE); txtshow.setText(detail); Toast.makeText(MainActivity.this, "HTML代码加载完毕", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show(); break; case 0x003: hideAllWidget(); webView.setVisibility(View.VISIBLE); webView.loadDataWithBaseURL("", detail, "text/html", "UTF-8", ""); Toast.makeText(MainActivity.this, "网页加载完毕", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show(); break; default: break; } } ; }; @Override protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); setContentView(R.layout.activity_main); setViews(); } private void setViews() { txtMenu = (TextView) findViewById(R.id.txtMenu); txtshow = (TextView) findViewById(R.id.txtshow); imgPic = (ImageView) findViewById(R.id.imgPic); webView = (WebView) findViewById(R.id.webView); scroll = (ScrollView) findViewById(R.id.scroll); registerForContextMenu(txtMenu); } // 定义一个隐藏所有控件的方法: private void hideAllWidget() { imgPic.setVisibility(View.GONE); scroll.setVisibility(View.GONE); webView.setVisibility(View.GONE); } @Override // 重写上下文菜单的创建方法 public void onCreateContextMenu(ContextMenu menu, View v, ContextMenu.ContextMenuInfo menuInfo) { MenuInflater inflator = new MenuInflater(this); inflator.inflate(R.menu.menus, menu); super.onCreateContextMenu(menu, v, menuInfo); } // 上下文菜单被点击是触发该方法 @Override public boolean onContextItemSelected(MenuItem item) { switch (item.getItemId()) { case R.id.one: new Thread() { public void run() { try { byte[] data = GetData.getImage(PIC_URL); bitmap = BitmapFactory.decodeByteArray(data, 0, data.length); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } handler.sendEmptyMessage(0x001); } ; }.start(); break; case R.id.two: new Thread() { public void run() { try { detail = GetData.getHtml(HTML_URL); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } handler.sendEmptyMessage(0x002); }; }.start(); break; case R.id.three: if (detail.equals("")) { Toast.makeText(MainActivity.this, "先请求HTML先嘛~", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show(); } else { handler.sendEmptyMessage(0x003); } break; } return true; }}最后别忘了加上联网权限:
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.INTERNET" />
注意事项:
用handler的原因就不用讲了吧~另外我们加载html代码的使用的是webView的loadDataWithBaseURL而非LoadData,如果用LoadData又要去纠结中文乱码的问题,so…用loadDataWithBaseURL就可以不用纠结那么多了另外有些页面可能需要我们提交一些参数,比如账号密码:我们只需把对应参数拼接到url尾部即可,比如:https://192.168.191.1:8080/ComentServer/LoginServlet?passwd=123&name=Jack然后服务端getParamater("passwd")这样就可以获得相应的参数了,我们请求时这些东西都会看得清清楚楚,所以说GET方式并不安全!另外还有一点要注意的就是Android从4.0开始就不允许在非UI线程中进行UI操作!
2)HttpURLConnection发送POST请求代码示例
有GET自然有POST,我们通过openConnection获取到的HttpURLConnection默认是进行Get请求的,所以我们使用POST提交数据,应提前设置好相关的参数:conn.setRequestMethod("POST");还有:conn.setDoOutput(true);conn.setDoInput(true);设置允许输入,输出还有:conn.setUseCaches(false); POST方法不能缓存,要手动设置为false,具体实现看代码:
运行效果图:
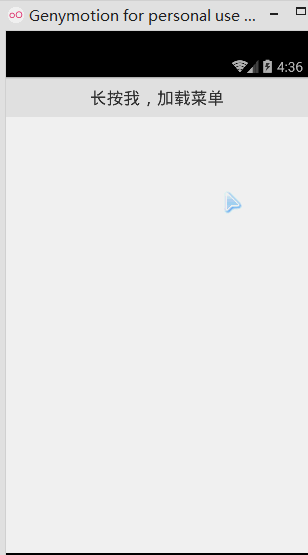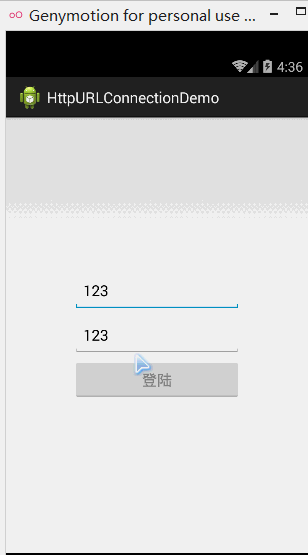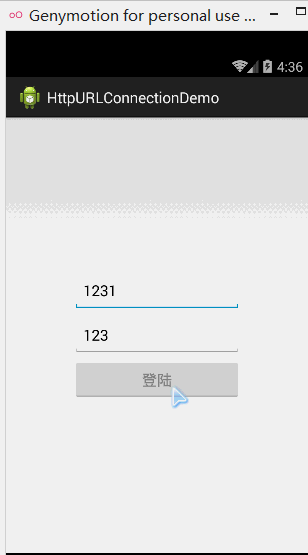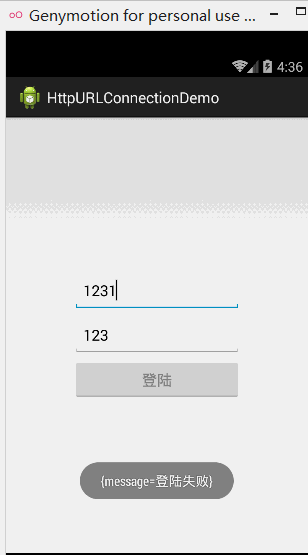
核心代码:
PostUtils.java
public class PostUtils { public static String LOGIN_URL = "https://172.16.2.54:8080/HttpTest/ServletForPost"; public static String LoginByPost(String number,String passwd) { String msg = ""; try{ HttpURLConnection conn = (HttpURLConnection) new URL(LOGIN_URL).openConnection(); //设置请求方式,请求超时信息 conn.setRequestMethod("POST"); conn.setReadTimeout(5000); conn.setConnectTimeout(5000); //设置运行输入,输出: conn.setDoOutput(true); conn.setDoInput(true); //Post方式不能缓存,需手动设置为false conn.setUseCaches(false); //我们请求的数据: String data = "passwd="+ URLEncoder.encode(passwd, "UTF-8")+ "&number="+ URLEncoder.encode(number, "UTF-8"); //这里可以写一些请求头的东东... //获取输出流 OutputStream out = conn.getOutputStream(); out.write(data.getBytes()); out.flush(); if (conn.getResponseCode() == 200) { // 获取响应的输入流对象 InputStream is = conn.getInputStream(); // 创建字节输出流对象 ByteArrayOutputStream message = new ByteArrayOutputStream(); // 定义读取的长度 int len = 0; // 定义缓冲区 byte buffer[] = new byte[1024]; // 按照缓冲区的大小,循环读取 while ((len = is.read(buffer)) != -1) { // 根据读取的长度写入到os对象中 message.write(buffer, 0, len); } // 释放资源 is.close(); message.close(); // 返回字符串 msg = new String(message.toByteArray()); return msg; } }catch(Exception e){e.printStackTrace();} return msg; }}PS:因为电脑没装MyEclipse,而且时间关系,就不另外写demo了,用回之前的Eclipse的那个demo!其实从直接看核心代码就够了~代码下载:HttpURLConnection例子.zip
4.Cookie问题的处理
说这个之前,首先我们要理解两个概念:Session和CookieCookie只是Session机制的一种常用形式,我们也可以使用其他方式来作为客户端的一个唯一标识,这个由服务器决定,唯一能够证明一个客户端标识就好!除了这种方式外,我们还可以使用URL重写!方法来实现!所以以后别傻傻的跟别人说:Session不就是Cookie!
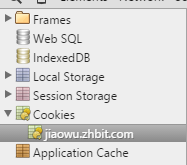
下面通过一个例子来帮助大家理解这个Cookie:小猪输入账号密码后登陆下学校的教务系统,然后访问课表信息成功,然后如果你用的是Chrome,按F12进入开发模式:来到Resources界面可以看到我们的Cookies:
点击后我们可以看到里面保存的内容,由名称;值;cookie所在的域(domain);cookie所在的目录(path)Asp.net默认为/即根目录;过期时间;Cookie大小:
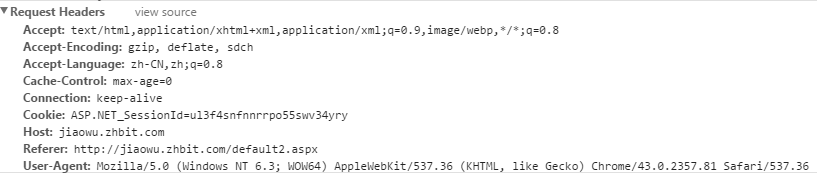
我们可以看到请求头中有一个Cookie的字段:
恩呢,现在我们把Cookie清掉(或者等几分钟),然后再访问下述链接:
这时候,页面竟然自动跳回登陆页面了!当然一些其他的网站可能会弹出一个对话框说"登陆超时"之类的东西!
小结下Http请求登陆的一个简单流程:一般是登陆的时候:服务器通过Set-Cookie响应头,返回一个Cookie,浏览器默认保存这个Cookie,后续访问相关页面的时候会带上这个Cookie,通过Cookie请求头来完成访问,如果没Cookie或者Cookie过期,就提示用户没登陆,登陆超时,访问需要登陆之类的信息!
而我们使用HttpClient和HttpURLConnection其实也就是模拟这一个流程,登陆后拿到cookie拿着它去发送请求:关键代码如下:获得Cookie:conn.getHeaderField("Set-Cookie");请求时带上Cookie:conn.setRequestProperty("Cookie",cookie);
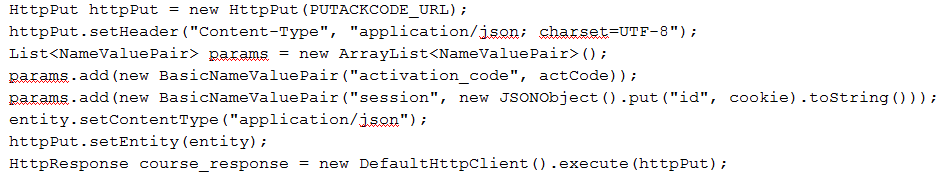
另外,除了这种设置请求头的方式外,还可以用另一种折衷的方法:URL重写:就是在原先请求链接的基础上,加上一个…&sessionid=xxxxx这样的参数,然后由服务器来解析判断!Get可以这么写,而Post写法如下:
这里我们用的是JSON字符串的形式,接到请求时服务端取出session里的内容,然后做下查询即可~
5.使用HttpURLConnection发送PUT请求
Put请求对于很多朋友来说可能有点陌生,毕竟我们平时接触的比较多的情况都是GET和POST,一开始小猪也不知道,不过后来才发现和POST其实是差不多的,而且我们只需在POST的基础上改点东西就可以使用了!而HttpClient也给我们提供了一个HttpPut的API,下面贴下小猪自己项目中写的请求代码:
public static String LoginByPut(Context mContext, String mobile, String password, int from, String devid,String version_name, int remember_me) { String resp = ""; try { HttpURLConnection conn = (HttpURLConnection) new URL(LOGIN_URL).openConnection(); conn.setRequestMethod("PUT"); conn.setReadTimeout(5000); conn.setConnectTimeout(5000); conn.setDoOutput(true); conn.setDoInput(true); conn.setUseCaches(false); String data = "mobile=" + mobile + "&password=" + password + "&from=" + from + "&devid=" + "devid" + "&version_name=" + "version_name" + "&remember_me=" + remember_me; ; // 获取输出流: OutputStreamWriter writer = new OutputStreamWriter(conn.getOutputStream()); writer.write(data); writer.flush(); writer.close(); // 获取相应流对象: InputStream in = conn.getInputStream(); BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(in)); StringBuilder response = new StringBuilder(); String line; while ((line = reader.readLine()) != null) response.append(line); SPUtils.put(mContext, "session", conn.getHeaderField("Set-Cookie")); // 资源释放: in.close(); // 返回字符串 Log.e("HEHE", response.toString()); return response.toString(); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } return "";}本节小结:
好的,本节关于HttpUrlConnection的使用介绍就到这里,另外,HTTP这一小节大部分来自于小猪以前写的一个小合集Android之Http通信,如果看过这个系列的可以跳过这节,大部分内容都是一样的!嗯,就说这么多,谢谢~